(no subject)
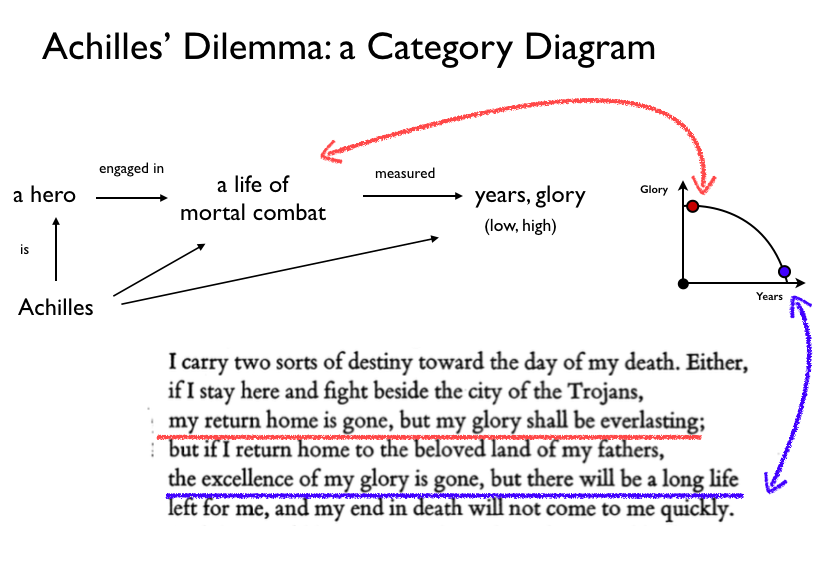
Homer invented Odysseus as a breakthrough solution to the Achilles dilemma. Now, inspired by Homer, the Greek polis invents the hoplite and phalanx to achieve the same breakthrough in real life.
https://youtu.be/TuJ7lGZVUl4?t=469

“ In time, the sheep began to accord with the animal that gamboled in Bakewell’s mind. He stopped touring England to buy rams. Instead, he employed a strategy known as in-and-in breeding. Bakewell mated cousin to cousin, brother to sister, father to daughter. Other farmers thought him mad because they believed inbreeding invariably led to disaster. That might be true for other farmers, but not for Bakewell. He was able to make sure that all the qualities he wanted in his sheep became fixed in his flock, but none of the deformities that might ruin his new breed.
With a flock of just a few hundred New Leicester, Bakewell couldn’t feed the millions of hungry English. Instead, he sold his sheep to other breeders, who started their own New Leicester flocks. They paid him dearly. They were even willing to do something that had previously been unheard-of: They would rent his rams for their services. Bakewell sent the rams to their appointments in two-wheel sprung carriages, suspended inside from slings. He claimed the right to take the best lambs produced by his rented rams, improving his own flock even more.
She Has Her Mother's Laugh.
On nearly all of the virtues which the tradition touches, the Confucians show their
characteristic attention to the potential trade-offs between love and a sense of
obligation, natural spontaneity and reverence, and unselfconsciousness and selfcontrol.
...
Virtue ethics in this sense has to do with the way that ethical norms
are derived or explained. It presupposes that virtue (or perhaps approximate notions
like flourishing) is more basic than rules of action and the maximization of good
states of affairs. Whereas a consequentialist might say that keeping a promise to a
friend is right because it gives rise to the greatest possible amount of happiness or
well-being, a virtue ethicist might say it is right because it is honest or trustworthy, or
simply because it is what a person of admirable character would do.
CONFUCIANISM AND VIRTUE ETHICS:
STILL A FLEDGLING IN CHINESE AND COMPARATIVE PHILOSOPHY
JUSTIN TIWALD
https://scholarworks.sjsu.edu/comparativephilosophy/vol1/iss2/7/
Comparative Philosophy Volume 1, No. 2 (2010): 55-63
Open Access / ISSN 2151-6014
“With the ending of hostilities the position in Rome with regard to supplies became easier. Grain was imported from Campania and most people, now that the threat of famine had passed, brought out what they had hoarded. Peace and plenty were accompanied, however, by a return of popular discontent, and, troubles abroad having ceased, fresh causes for them were sought at home.”
-- Titus Livy. “The Early History of Rome.”
“Faced by this storm the consuls quickly realized the insecurity of high position unsupported by force. ”

Чем сильнее формализация системы, тем больше усилий требуется для её интерпретации и понимания. То, что мы выигрываем на экономичности формальных процедур, мы теряем в понятности. Как только создается формальная система, возникают неучитываемые ею аспекты реальности, с которыми эту систему требуется сложным образом соотносить (или забывать об этих «неудобных» реалиях).
Любарский, Г.Ю. Рождение Науки.


This increase in powers of representation is thus qualified by a positivist disclaimer, by an implicit and generalized footnote that accompanies all scientific work. It states that we know nothing of reality because all we have are models that are constructed by us.
A. Nordmann. Collapse of Distance: Epistemic Strategies of Science and Technoscience. 2006.
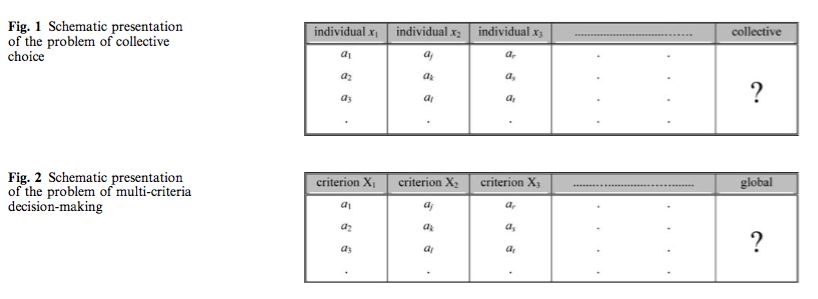
As soon as the number of options to choose from is equal to or greater than three, and the number of criteria considered relevant is at least two, no satisfactory global decision function, in the sense of a function satisfying all five requirements mentioned, can be found.
“
We spend our time looking for threats against a company. We look for things that might be active inside the company that would cause us concern, and then of course we look to respond—detecting, containing, and deflecting those threats as much as possible while at the same time keeping in mind that our executives and board of directors always want to know what's going on with security in the company.
Generically, every breach has the big data problem. For example, in a malware incident that results in a breach, the malware comes in and spreads across the environment.
When that scope [of investigation] expands, the security team typically has to deal with a sudden increase in big data -- logs, alerts, etc. -- making budget planning critical. Right now I'm planning my budget for next year, and I hope I ask for enough disk space and computing power so that the infrastructure is prepared for future attacks. ... Burst capacity is really critical for the security team who needs to find answers quickly.
An opportunity cost will usually arise whenever an economic agent chooses between alternative ways of allocating scarce resources. The opportunity cost of such a decision is the value of the next best alternative use of scarce resources. Opportunity cost can be illustrated by using production possibility frontiers (PPFs) which provide a simple, yet powerful tool to illustrate the effects of making an economic choice.
A PPF shows all the possible combinations of two goods, or two options available at one point in time.
Mythica, which is a hypothetical economy, produces only two goods - textbooks and computers. When it uses all of its resources, it can produce five million computers and fifty five million textbooks. In fact, it can produce all the following combinations of computers and books.
| COMPUTERS (m) | TEXTBOOKS (m) |
| 0 | 70 |
| 1 | 69 |
| 2 | 68 |
| 3 | 65 |
| 4 | 60 |
| 5 | 55 |
| 6 | 48 |
| 7 | 39 |
| 8 | 24 |
| 9 | 0 |
